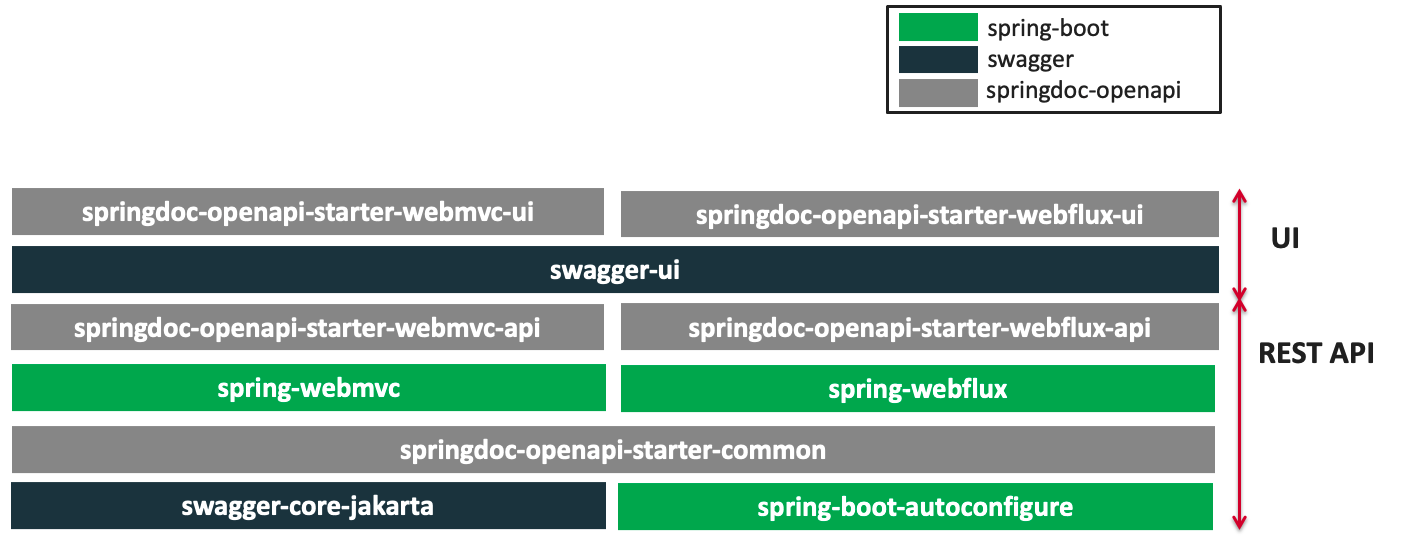
Springdoc-openapi Modules
Spring WebMvc support
-
Documentation will be available at the following url for json format:
http://server:port/context-path/v3/api-docs-
server: The server name or IP
-
port: The server port
-
context-path: The context path of the application
-
-
Documentation will be available in yaml format as well, on the following path : /v3/api-docs.yaml
-
Add the library to the list of your project dependencies. (No additional configuration is needed)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-api</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>| This dependency is relevant if you want to generate the OpenAPI description without using the swagger-ui or Scalar. |
| For custom path of the OpenAPI documentation in Json format, add a custom springdoc property, in your spring-boot configuration file: |
# /api-docs endpoint custom path
springdoc.api-docs.path=/api-docsSpring WebFlux support
-
Documentation will be available in yaml format as well, on the following path : /v3/api-docs.yaml
-
Add the library to the list of your project dependencies (No additional configuration is needed)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-api</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>Swagger-UI support
Swagger UI allows anyone — be it your development team or your end consumers — to visualize and interact with the API’s resources without having any of the implementation logic in place. It’s automatically generated from your OpenAPI (formerly known as Swagger) Specification, with the visual documentation making it easy for back end implementation and client side consumption.
-
If your project is using
spring-boot-starter-weband you need the access to the swagger-ui, add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>-
If your project is using
spring-boot-starter-webfluxand you need the access to the swagger-ui, add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>Scalar support
Scalar is an open-source API platform, designed for creating beautiful, interactive API documentation and providing a built-in REST API client, with first-class support for OpenAPI (formerly Swagger) specifications. It’s particularly aimed at improving the developer experience when exploring APIs.
springdoc-openapi extends Scalar configuration to make it compatible with Spring Boot applications.
You can rely on native Scalar configuration properties, using the prefix scalar, as explained in the Scalar documentation.
-
The Swagger UI page will then be available at
http://server:port/context-path/scalarand the OpenAPI description will be available at the following url for json format:http://server:port/context-path/v3/api-docs-
server: The server name or IP
-
port: The server port
-
context-path: The context path of the application
-
-
If your project is using
spring-boot-starter-weband you need the access to the swagger-ui, add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-scalar</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>-
If your project is using
spring-boot-starter-webfluxand you need the access to the swagger-ui, add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-scalar</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
</dependency>Spring Hateoas support
The support for Spring Hateoas is available using the dependency springdoc-openapi-hateoas.
The projects that use spring-boot-starter-hateoas should use:
-
springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-apiif they need only the access to the OpenAPI endpoints -
OR
springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui, if they need also the access to the swagger-ui
Spring Data Rest support
springdoc-openapi project supports spring-boot-starter-data-rest types like: @RepositoryRestResource and QuerydslPredicate annotations.
The projects that use spring-boot-starter-data-rest should use:
-
springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-apiif they need only the access to the OpenAPI endpoints -
OR
springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui, if they need also the access to the swagger-ui
Spring Security support
springdoc-openapi helps ignoring @AuthenticationPrincipal type in case it is used on REST Controllers.
springdoc-openapi supports also exposing Oauth2 endpoints of spring-security-oauth2-authorization-server.
The projects that use spring-boot-starter-security or spring-security-oauth2-authorization-server should use:
-
springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-apiif they depend onspring-boot-starter-weband they only need the access to the OpenAPI endpoints. -
OR
springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-apiif they depend onspring-boot-starter-webfluxand they only the access to the OpenAPI endpoints.
Actuator support
-
In order to display
spring-boot-actuatorendpoints, simply add the following property:
springdoc.show-actuator=trueStarting from the release 1.5.1, it will be possible to expose the swagger-ui and the openapi endpoints on actuator port.
| The actuator management port has to be different from the application port. |
To expose the swagger-ui and Scalar, on the management port, you should set
springdoc.use-management-port=true
# This property enables the openapi and swagger-ui endpoints to be exposed beneath the actuator base path.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=openapi, swagger-ui
# This property enables the openapi and scalar endpoints to be exposed beneath the actuator base path.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=openapi, scalarOnce enabled, you should also be able to see the springdoc-openapi endpoints under: (host and port depends on your settings)
- http://serverName:managementPort/actuator
For example, if you have the following settings:
These endpoints will be available:
-
REST API that holdes the OpenAPI definition:
-
http://serverName:managementPort/actuator/openapi
-
-
An Endpoint, that routes to the swagger-ui:
-
http://serverName:managementPort/actuator/swagger-ui
-
-
Or An Endpoint, that routes to the scalar:
-
http://serverName:managementPort/actuator/scalar
-
management.server.port=9090For the example, you should also be able to see the springdoc-openapi endpoints depending on the chosen UI:
-
http://serverName:9090/actuator -
http://serverName:9090/actuator/swagger-uiorhttp://serverName:9090/actuator/scalar -
http://serverName:9090/actuator/openapi
All the path springdoc-openapi properties are not applicable when springdoc.use-management-port=true.
If you want to reach the application endpoints, from the swagger-ui/scalar deployed beneath the actuator base path, using a different port from your application, CORS for your endpoints on your application level should be enabled.
|
Additionally, it is also possible to combine this property, with the existing property to display the actuator endpoints in the swagger-ui/scalar.
springdoc.show-actuator=trueOnce enabled: - A dedicated group for the actuator endpoints will be by default added. - If no group is defined for the application, a default one will be added.
The swagger-ui will be then accessible through the actuator port:
-
http://serverName:managementPort/actuator/swagger-ui
The scalar UI will be then accessible through the actuator port:
-
http://serverName:managementPort/actuator/scalar
If the management port is different from the application port and springdoc.use-management-port is not defined but springdoc.show-actuator is set to true:
-
The swagger-ui will be then accessible through the application port. For example:
http://serverName:applicationPort/swagger-ui.html -
The scalar UI will be then accessible through the application port. For example:
http://serverName:applicationPort/scalar -
A dedicated group for the actuator endpoints will be by default added.
-
If no group is defined for the application, a default one will be added.
If you want to reach the actuator endpoints for this case (different port from your application), CORS for your actuator endpoints should be enabled.
|
Note: The naming of these new endpoints beneath the actuator base path cannot be customized for now.
Spring Cloud Function Web support
spring-cloud-function-web exposes Java Function as REST endpoint automatically.
* Since version v1.6.3, the support of functional endpoints has been added.
-
These starters will display the OpenAPI description of the
spring-cloud-function-webendpoints.-
If you are using
spring-web, simply add thespringdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-apidependency. -
If you are using
spring-webflux, simply add thespringdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-apidependency.
-
The customisation of the output can be achieved programmatically through OpenApiCustomizer or with the annotations: @RouterOperations and @RouterOperation.
For annotation usage, you have:
* @RouterOperation: It can be used alone, if the customisation is related to a single REST API.
When using @RouterOperation, it’s not mandatory to fill the path
-
@RouterOperation, contains the@Operationannotation. The@Operationannotation can also be placed on the bean method level if the property beanMethod is declared.
| Don’t forget to set operationId which is mandatory. |
@Bean
@RouterOperation(operation = @Operation(description = "Say hello", operationId = "hello", tags = "persons",
responses = @ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", content = @Content(schema = @Schema(implementation = PersonDTO.class)))))
public Supplier<PersonDTO> helloSupplier() {
return () -> new PersonDTO();
}
-
@RouterOperations: This annotation should be used to describe the multiple REST APIs exposed byspring-cloud-function-web. When usingRouterOperations, it’s mandatory to fill the method property. -
A
@RouterOperations, contains many@RouterOperation.
@Bean
@RouterOperations({
@RouterOperation(method = RequestMethod.GET, operation = @Operation(description = "Say hello GET", operationId = "lowercaseGET", tags = "persons")),
@RouterOperation(method = RequestMethod.POST, operation = @Operation(description = "Say hello POST", operationId = "lowercasePOST", tags = "positions"))
})
public Function<Flux<String>, Flux<String>> lowercase() {
return flux -> flux.map(value -> value.toLowerCase());
}
Some code samples are available on GITHUB of demos:
Kotlin support
springdoc-openapi supports Kotlin types.
The projects that use Kotlin should use:
-
springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-apiif they depend onspring-boot-starter-weband they only need the access to the OpenAPI endpoints. -
OR
springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-apiif they depend onspring-boot-starter-webfluxand they only the access to the OpenAPI endpoints.
In addition, your project should add jackson-module-kotlin as well to have the full support of Kotlin types:
|
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.module</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-module-kotlin</artifactId>
</dependency>Groovy support
The projects that use Groovy should use:
-
springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-apiif they depend onspring-boot-starter-weband they only need the access to the OpenAPI endpoints. -
OR
springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-apiif they depend onspring-boot-starter-webfluxand they only the access to the OpenAPI endpoints.
Javadoc support
springdoc-openapi can introspect Javadoc annotations and comments:
-
The javadoc comment of a method: is resolved as the
@Operationdescription -
@return: is resolved as the@Operationresponse description -
The javadoc comment of an attribute: is resolved as '@Schema' description for this field.
The projects that needs Javadoc support should use:
-
springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-apiif they depend onspring-boot-starter-weband they only need the access to the OpenAPI endpoints. -
OR
springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-apiif they depend onspring-boot-starter-webfluxand they only the access to the OpenAPI endpoints.
In addition, your project should add therapi-runtime-javadoc to read Javadoc comments at runtime.
Ensure that you add it as well as its annotation processor to your project’s dependencies. Otherwise, the Javadoc support will fail silently.
|
<!--Annotation processor -->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>com.github.therapi</groupId>
<artifactId>therapi-runtime-javadoc-scribe</artifactId>
<version>0.15.0</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<!-- Runtime library -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.therapi</groupId>
<artifactId>therapi-runtime-javadoc</artifactId>
<version>0.15.0</version>
</dependency>| If both a swagger-annotation description and a javadoc comment are present. The value of the swagger-annotation description will be used. |
Springdoc-openapi BOM
Starting from version v2.8.7, springdoc-openapi provides a BOM (Bill of Materials) to manage the dependencies of the project.
You can declare it in your project as follows:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-bom</artifactId>
<version>2.8.16</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>