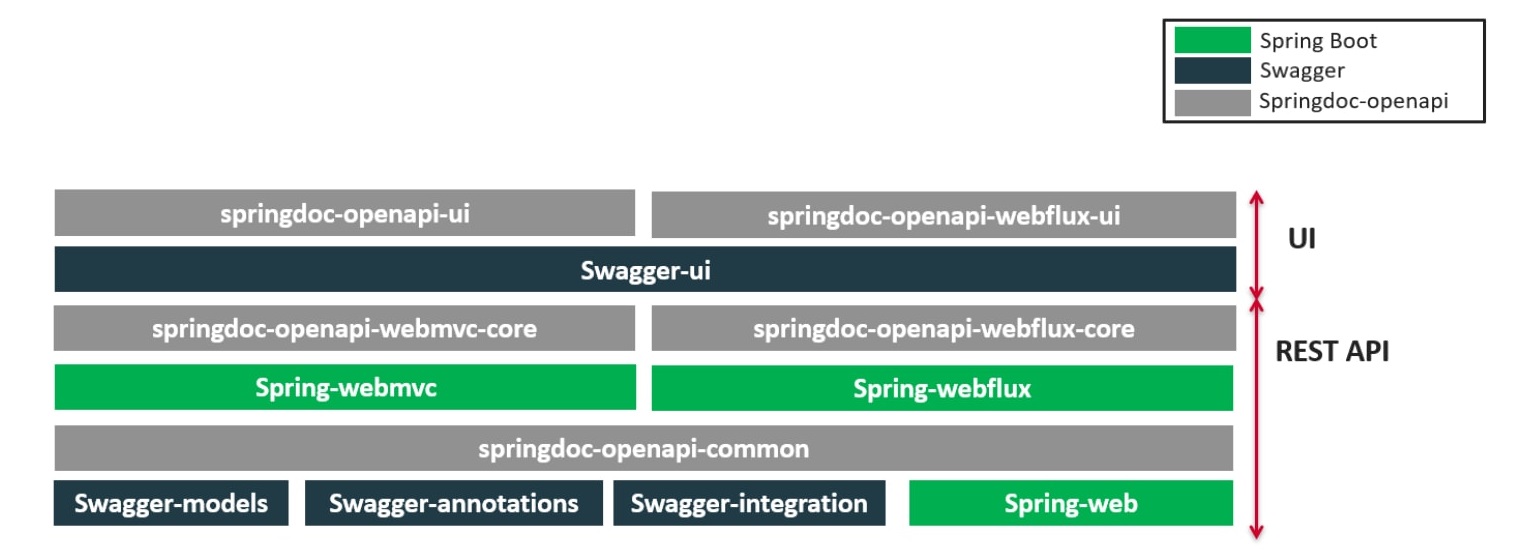
| For spring-boot v3 support, make sure you use springdoc-openapi v2 |
springdoc-openapi is on Open Collective. If you ❤️ this project consider becoming a sponsor.
This project is sponsored by
1. Introduction
springdoc-openapi java library helps to automate the generation of API documentation using spring boot projects.
springdoc-openapi works by examining an application at runtime to infer API semantics based on spring configurations, class structure and various annotations.
Automatically generates documentation in JSON/YAML and HTML format APIs. This documentation can be completed by comments using swagger-api annotations.
This library supports:
-
OpenAPI 3
-
Spring-boot (v1 and v2)
-
JSR-303, specifically for @NotNull, @Min, @Max, and @Size.
-
Swagger-ui
-
Scalar
-
OAuth 2
-
GraalVM native images
The following video introduces the Library:
This is a community-based project, not maintained by the Spring Framework Contributors (Pivotal).
2. Getting Started
For the integration between spring-boot and swagger-ui, add the library to the list of your project dependencies (No additional configuration is needed)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>This will automatically deploy swagger-ui to a spring-boot application:
-
Documentation will be available in HTML format, using the official swagger-ui jars
-
The Swagger UI page will then be available at
http://server:port/context-path/swagger-ui.htmland the OpenAPI description will be available at the following url for json format:http://server:port/context-path/v3/api-docs-
server: The server name or IP
-
port: The server port
-
context-path: The context path of the application
-
-
Documentation will be available in yaml format as well, on the following path : /v3/api-docs.yaml
| For custom path of the swagger documentation in HTML format, add a custom springdoc property, in your spring-boot configuration file: . |
# swagger-ui custom path
springdoc.swagger-ui.path=/swagger-ui.html3. Springdoc-openapi Modules
3.2. Spring WebMvc support
-
Documentation will be available at the following url for json format:
http://server:port/context-path/v3/api-docs-
server: The server name or IP
-
port: The server port
-
context-path: The context path of the application
-
-
Documentation will be available in yaml format as well, on the following path : /v3/api-docs.yaml
-
Add the library to the list of your project dependencies. (No additional configuration is needed)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-webmvc-core</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>| This dependency is relevant if you want to generate the OpenAPI description without using the swagger-ui. |
| For custom path of the OpenAPI documentation in Json format, add a custom springdoc property, in your spring-boot configuration file: |
# /api-docs endpoint custom path
springdoc.api-docs.path=/api-docs3.3. Spring WebFlux support
-
Documentation will be available in yaml format as well, on the following path : /v3/api-docs.yaml
-
Add the library to the list of your project dependencies (No additional configuration is needed)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-webflux-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>3.4. Spring Hateoas support
The support for Spring Hateoas is available using the dependency springdoc-openapi-hateoas. The projects that use Spring Hateoas should combine this dependency with the springdoc-openapi-ui dependency. This dependency enables the support of Spring Hateoas format.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-hateoas</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>3.5. Spring Data Rest support
The projects that use spring-data-rest can add the following dependency in combination with the springdoc-openapi-ui dependency.
This dependency enables the support of spring-boot-starter-data-rest types like: @RepositoryRestResource and QuerydslPredicate annotations.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-data-rest</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>3.6. Spring Security support
For a project that uses spring-security, you should add the following dependency, in combination with the springdoc-openapi-ui dependency: This dependency helps ignoring @AuthenticationPrincipal in case its used on REST Controllers.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-security</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>3.7. Actuator support
-
In order to display
spring-boot-actuatorendpoints, simply add the following property:
springdoc.show-actuator=trueStarting from the release 1.5.1, it will be possible to expose the swagger-ui and the openapi endpoints on actuator port.
| The actuator management port has to be different from the application port. |
To expose the swagger-ui, on the management port, you should set
springdoc.use-management-port=true
# This property enables the openapi and swagger-ui endpoints to be exposed beneath the actuator base path.
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=openapi, swagger-uiOnce enabled, you should also be able to see the springdoc-openapi endpoints under: (host and port depends on your settings)
- http://serverName:managementPort/actuator
For example, if you have the following settings:
Two endpoints will be available:
-
REST API that holdes the OpenAPI definition:
-
http://serverName:managementPort/actuator/openapi
-
-
An Endpoint, that routes to the swagger-ui:
-
http://serverName:managementPort/actuator/swagger-ui
-
management.server.port=9090For the example, you should also be able to see the springdoc-openapi endpoints:
-
http://serverName:9090/actuator -
http://serverName:9090/actuator/swagger-ui -
http://serverName:9090/actuator/openapi
All the path springdoc-openapi properties are not applicable when springdoc.use-management-port=true.
If you want to reach the application endpoints, from the swagger-ui deployed beneath the actuator base path, using a different port from your application, CORS for your endpoints on your application level should be enabled.
|
Additionally, it is also possible to combine this property, with the existing property to display the actuator endpoints in the swagger-ui.
springdoc.show-actuator=trueOnce enabled: - A dedicated group for the actuator endpoints will be by default added. - If no group is defined for the application, a default one will be added.
The swagger-ui will be then accessible through the actuator port:
-
http://serverName:managementPort/actuator/swagger-ui
If the management port is different from the application port and springdoc.use-management-port is not defined but springdoc.show-actuator is set to true:
-
The swagger-ui will be then accessible through the application port. For example:
http://serverName:applicationPort/swagger-ui.html -
A dedicated group for the actuator endpoints will be by default added.
-
If no group is defined for the application, a default one will be added.
If you want to reach the actuator endpoints for this case (different port from your application), CORS for your actuator endpoints should be enabled.
|
Note: The naming of these new endpoints beneath the actuator base path cannot be customized for now.
3.8. Spring Cloud Function Web support
spring-cloud-function-web exposes Java Function as REST endpoint automatically.
* Since version v1.6.3, the support of functional endpoints has been added.
-
These starters will display the OpenAPI description of the
spring-cloud-function-webendpoints.-
If you are using
spring-web, simply add thespringdoc-openapi-uidependency. -
If you are using
spring-webflux, simply add thespringdoc-openapi-webflux-uidependency.
-
The customisation of the output can be achieved programmatically through OpenApiCustomizer or with the annotations: @RouterOperations and @RouterOperation.
For annotation usage, you have:
* @RouterOperation: It can be used alone, if the customisation is related to a single REST API.
When using @RouterOperation, it’s not mandatory to fill the path
-
@RouterOperation, contains the@Operationannotation. The@Operationannotation can also be placed on the bean method level if the property beanMethod is declared.
| Don’t forget to set operationId which is mandatory. |
@Bean
@RouterOperation(operation = @Operation(description = "Say hello", operationId = "hello", tags = "persons",
responses = @ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", content = @Content(schema = @Schema(implementation = PersonDTO.class)))))
public Supplier<PersonDTO> helloSupplier() {
return () -> new PersonDTO();
}
-
@RouterOperations: This annotation should be used to describe the multiple REST APIs exposed byspring-cloud-function-web. When usingRouterOperations, it’s mandatory to fill the method property. -
A
@RouterOperations, contains many@RouterOperation.
@Bean
@RouterOperations({
@RouterOperation(method = RequestMethod.GET, operation = @Operation(description = "Say hello GET", operationId = "lowercaseGET", tags = "persons")),
@RouterOperation(method = RequestMethod.POST, operation = @Operation(description = "Say hello POST", operationId = "lowercasePOST", tags = "positions"))
})
public Function<Flux<String>, Flux<String>> lowercase() {
return flux -> flux.map(value -> value.toLowerCase());
}
Some code samples are available on GITHUB of demos:
3.9. Kotlin support
For a project that uses Kotlin, you should add the following dependency. This dependency improves the support of Kotlin types:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-kotlin</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>-
If you are using spring-web, you should combine the
springdoc-openapi-kotlinmodule withspringdoc-openapi-ui. -
If you are using spring-webflux, you should combine the
springdoc-openapi-kotlinmodule withspringdoc-openapi-webflux-ui.
3.10. Groovy support
For a project that uses Groovy, you should add the following dependency, in combination with the springdoc-openapi-ui dependency: This dependency improves the support of Kotlin types:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-groovy</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>3.11. Javadoc support
For a project that wants to enable javadoc support, you should add the following dependency, in combination with the springdoc-openapi-ui dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-javadoc</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>This dependency improves the support of javadoc tags and comments:
-
The javadoc comment of a method: is resolved as the
@Operationdescription -
@return: is resolved as the@Operationresponse description -
The javadoc comment of an attribute: is resolved as '@Schema' description for this field.
This dependency is based on the library therapi-runtime-javadoc
Make sure, you enable the annotation processor of therapi-runtime-javadoc in order to enable javadoc support for springdoc-openapi.
|
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>com.github.therapi</groupId>
<artifactId>therapi-runtime-javadoc-scribe</artifactId>
<version>0.15.0</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>| If both a swagger-annotation description and a javadoc comment are present. The value of the swagger-annotation description will be used. |
4. Springdoc-openapi Features
4.1. Adding API Information and Security documentation
The library uses spring-boot application auto-configured packages to scan for the following annotations in spring beans: OpenAPIDefinition and Info. These annotations declare, API Information: Title, version, licence, security, servers, tags, security and externalDocs. For better performance of documentation generation, declare @OpenAPIDefinition and @SecurityScheme annotations within a spring managed bean.
4.2. Error Handling for REST using @ControllerAdvice
To generate documentation automatically, make sure all the methods declare the HTTP Code responses using the annotation: @ResponseStatus
4.3. Disabling the springdoc-openapi endpoints
In order to disable the springdoc-openapi endpoint (/v3/api-docs by default) use the following property:
# Disabling the /v3/api-docs endpoint
springdoc.api-docs.enabled=false4.4. Disabling the swagger-ui
In order to disable the swagger-ui, use the following property:
# Disabling the swagger-ui
springdoc.swagger-ui.enabled=false4.5. Swagger-ui configuration
The library supports the swagger-ui official properties:
You need to declare swagger-ui properties as spring-boot properties. All these properties should be declared with the following prefix: springdoc.swagger-ui
4.6. Selecting the Rest Controllers to include in the documentation
Additionally, to @Hidden annotation from swagger-annotations, its possible to restrict the generated OpenAPI description using package or path configuration.
For the list of packages to include, use the following property:
# Packages to include
springdoc.packagesToScan=com.package1, com.package2For the list of paths to include, use the following property:
# Paths to include
springdoc.pathsToMatch=/v1, /api/balance/**4.7. Spring-webflux/WebMvc.fn with Functional Endpoints
Since version v1.5.0, a functional DSL has been introduced, thanks to this enhancement in the spring-framework: #25938
It’s an alternative functional API to the @RouterOperations annotations.
This is a sample DSL, to generate OpenAPI description to the webflux/WebMvc.fn REST endpoints:
@Bean
RouterFunction<?> routes() {
return route().GET("/foo", HANDLER_FUNCTION, ops -> ops
.operationId("hello")
.parameter(parameterBuilder().name("key1").description("My key1 description"))
.parameter(parameterBuilder().name("key2").description("My key2 description"))
.response(responseBuilder().responseCode("200").description("This is normal response description"))
.response(responseBuilder().responseCode("404").description("This is another response description"))
).build();
}
Here is the link for some sample codes:
And the Demo code, using the functional endpoints DSL:
Since version v1.3.8, the support of functional endpoints has been added.
Two main annotations have been added for this purpose: @RouterOperations and @RouterOperation.
Only REST APIs with the @RouterOperations and @RouterOperation can be displayed on the swagger-ui.
-
@RouterOperation: It can be used alone, if the Router bean contains one single route related to the REST API.. When using @RouterOperation, its not mandatory to fill the path -
@RouterOperation, can reference directly a spring Bean (beanClass property) and the underlying method (beanMethod property): Springdoc-openapi, will then inspect this method and the swagger annotations on this method level.
@Bean
@RouterOperation(beanClass = EmployeeService.class, beanMethod = "findAllEmployees")
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> getAllEmployeesRoute() {
return route(GET("/employees").and(accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)),
req -> ok().body(
employeeService().findAllEmployees(), Employee.class));
}
-
@RouterOperation, contains the@Operationannotation. The@Operationannotation can also be placed on the bean method level if the property beanMethod is declared.
| Don’t forget to set operationId which is mandatory. |
@Bean
@RouterOperation(operation = @Operation(operationId = "findEmployeeById", summary = "Find purchase order by ID", tags = { "MyEmployee" },
parameters = { @Parameter(in = ParameterIn.PATH, name = "id", description = "Employee Id") },
responses = { @ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", description = "successful operation", content = @Content(schema = @Schema(implementation = Employee.class))),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "400", description = "Invalid Employee ID supplied"),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "Employee not found") }))
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> getEmployeeByIdRoute() {
return route(GET("/employees/{id}"),
req -> ok().body(
employeeRepository().findEmployeeById(req.pathVariable("id")), Employee.class));
}
-
@RouterOperations: This annotation should be used if the Router bean contains multiple routes. When using RouterOperations, its mandatory to fill the path property. -
A
@RouterOperations, contains many@RouterOperation.
@RouterOperations({ @RouterOperation(path = "/getAllPersons", beanClass = PersonService.class, beanMethod = "getAll"),
@RouterOperation(path = "/getPerson/{id}", beanClass = PersonService.class, beanMethod = "getById"),
@RouterOperation(path = "/createPerson", beanClass = PersonService.class, beanMethod = "save"),
@RouterOperation(path = "/deletePerson/{id}", beanClass = PersonService.class, beanMethod = "delete") })
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> personRoute(PersonHandler handler) {
return RouterFunctions
.route(GET("/getAllPersons").and(accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::findAll)
.andRoute(GET("/getPerson/{id}").and(accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_STREAM_JSON)), handler::findById)
.andRoute(POST("/createPerson").and(accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::save)
.andRoute(DELETE("/deletePerson/{id}").and(accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::delete);
}
All the documentations filled using @RouterOperation, might be completed by the router function data.
For that, @RouterOperation fields must help identify uniquely the concerned route.
springdoc-openpi scans for a unique route related to a @RouterOperation annotation, using on the following criteria:
-
by path
-
by path and RequestMethod
-
by path and produces
-
by path and consumes
-
by path and RequestMethod and produces
-
by path and RequestMethod and consumes
-
by path and produces and consumes
-
by path and RequestMethod and produces and consumes
Some code samples are available on GITHUB of demos:
And some project tests: (from app69 to app75)
5. Springdoc-openapi Properties
springdoc-openapi relies on standard spring configuration properties (yml or properties) using the standard files locations.
5.1. springdoc-openapi core properties
| Parameter name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
springdoc.api-docs.path |
|
|
springdoc.api-docs.enabled |
|
|
springdoc.packages-to-scan |
|
|
springdoc.paths-to-match |
|
|
springdoc.produces-to-match |
|
|
springdoc.headers-to-match |
|
|
springdoc.consumes-to-match |
|
|
springdoc.paths-to-exclude |
|
|
springdoc.packages-to-exclude |
|
|
springdoc.default-consumes-media-type |
|
|
springdoc.default-produces-media-type |
|
|
springdoc.cache.disabled |
|
|
springdoc.show-actuator |
|
|
springdoc.auto-tag-classes |
|
|
springdoc.model-and-view-allowed |
|
|
springdoc.override-with-generic-response |
|
|
springdoc.group-configs[0].group |
|
|
springdoc.group-configs[0].display-name |
|
|
springdoc.group-configs[0].packages-to-scan |
|
|
springdoc.group-configs[0].paths-to-match |
|
|
springdoc.group-configs[0].paths-to-exclude |
`` |
|
springdoc.group-configs[0].packages-to-exclude |
|
|
springdoc.group-configs[0].produces-to-match |
|
|
springdoc.group-configs[0].consumes-to-match |
|
|
springdoc.group-configs[0].headers-to-match |
|
|
springdoc.api-docs.resolve-schema-properties |
|
|
springdoc.remove-broken-reference-definitions |
|
|
springdoc.writer-with-default-pretty-printer |
|
|
springdoc.model-converters.deprecating-converter.enabled |
|
|
springdoc.model-converters.polymorphic-converter.enabled |
|
|
springdoc.model-converters.pageable-converter.enabled |
|
|
springdoc.model-converters.sort-converter.enabled |
|
|
springdoc.use-fqn |
|
|
springdoc.show-login-endpoint |
|
|
springdoc.pre-loading-enabled |
|
|
springdoc.pre-loading-locales |
|
|
springdoc.writer-with-order-by-keys |
|
|
springdoc.use-management-port |
|
|
springdoc.disable-i18n |
|
|
springdoc.show-spring-cloud-functions |
|
|
springdoc.api-docs.version |
|
|
springdoc.default-flat-param-object |
|
|
springdoc.default-support-form-data |
|
|
springdoc.nullable-request-parameter-enabled |
|
|
springdoc.show-oauth2-endpoints |
|
|
springdoc.api-docs.resolve-extensions-properties |
|
|
springdoc.enable-default-api-docs |
|
|
springdoc.trim-kotlin-indent |
|
|
5.2. swagger-ui properties
-
The support of the swagger-ui properties is available on
springdoc-openapi. See Official documentation. -
You can use the same swagger-ui properties in the documentation as Spring Boot properties.
All these properties should be declared with the following prefix: springdoc.swagger-ui
|
| Parameter name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
springdoc.swagger-ui.path |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.enabled |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.configUrl |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.layout |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.validatorUrl |
By default, Swagger UI does not validate specs. You can use this parameter to set a validator URL, for example for against swagger.io’s online validator. |
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.tryItOutEnabled |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.filter |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.operationsSorter |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.tagsSorter |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth2RedirectUrl |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.displayOperationId |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.displayRequestDuration |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.deepLinking |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.defaultModelsExpandDepth |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.defaultModelExpandDepth |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.defaultModelRendering |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.docExpansion |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.maxDisplayedTags |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.showExtensions |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.url |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.showCommonExtensions |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.supportedSubmitMethods |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.queryConfigEnabled |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth. additionalQueryStringParams |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.disable-swagger-default-url |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.urls[0].url |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.urls[0].name |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.urlsPrimaryName |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth.clientId |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth.clientSecret |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth.realm |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth.appName |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth.scopeSeparator |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth.scopes |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.csrf.enabled |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.csrf.use-local-storage |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.csrf.use-session-storage |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.csrf.cookie-name |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.csrf.header-name |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.syntaxHighlight.activated |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.syntaxHighlight.theme |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth. useBasicAuthentication WithAccessCodeGrant |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.oauth. usePkceWithAuthorization CodeGrant |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.persistAuthorization |
|
|
springdoc.swagger-ui.use-root-path |
|
|
6. Springdoc-openapi Plugins
6.1. Maven plugin
The aim of springdoc-openapi-maven-plugin is to generate json and yaml OpenAPI description during build time.
The plugin works during integration-tests phase, and generate the OpenAPI description.
The plugin works in conjunction with spring-boot-maven plugin.
You can test it during the integration tests phase using the maven command:
mvn verifyIn order to use this functionality, you need to add the plugin declaration on the plugins section of your pom.xml:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot-maven-plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<jvmArguments>-Dspring.application.admin.enabled=true</jvmArguments>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>start</goal>
<goal>stop</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.5</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>integration-test</id>
<goals>
<goal>generate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>For more custom settings of the springdoc-openapi-maven-plugin, you can consult the plugin documentation:
6.2. Gradle plugin
This plugin allows you to generate an OpenAPI 3 specification for a Spring Boot application from a Gradle build.
plugins {
id("org.springframework.boot") version "2.7.0"
id("org.springdoc.openapi-gradle-plugin") version "1.9.0"
}
When you add this plugin and its runtime dependency plugins to your build file, the plugin creates the following tasks:
-
forkedSpringBootRun
-
generateOpenApiDocs
gradle clean generateOpenApiDocsFor more custom configuration of springdoc-openapi-gradle-plugin ,you can consult the plugin documentation:
7. Springdoc-openapi Demos
8. Migrating from SpringFox
-
Remove springfox and swagger 2 dependencies. Add
springdoc-openapi-uidependency instead.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-ui</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>-
Replace swagger 2 annotations with swagger 3 annotations (it is already included with
springdoc-openapi-uidependency). Package for swagger 3 annotations isio.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.-
@Api→@Tag -
@ApiIgnore→@Parameter(hidden = true)or@Operation(hidden = true)or@Hidden -
@ApiImplicitParam→@Parameter -
@ApiImplicitParams→@Parameters -
@ApiModel→@Schema -
@ApiModelProperty(allowEmptyValue = true)→@Schema(nullable = true) -
@ApiModelProperty→@Schema -
@ApiOperation(value = "foo", notes = "bar")→@Operation(summary = "foo", description = "bar") -
@ApiParam→@Parameter -
@ApiResponse(code = 404, message = "foo")→@ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "foo")
-
-
If you’re using an object to capture multiple request query params, annotation that method argument with
@ParameterObject -
This step is optional: Only if you have multiple
Docketbeans replace them withGroupedOpenApibeans.
Before:
@Bean
public Docket publicApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("org.github.springshop.web.public"))
.paths(PathSelectors.regex("/public.*"))
.build()
.groupName("springshop-public")
.apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
@Bean
public Docket adminApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("org.github.springshop.web.admin"))
.paths(PathSelectors.regex("/admin.*"))
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.withMethodAnnotation(Admin.class))
.build()
.groupName("springshop-admin")
.apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
Now:
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi publicApi() {
return GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.group("springshop-public")
.pathsToMatch("/public/**")
.build();
}
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi adminApi() {
return GroupedOpenApi.builder()
.group("springshop-admin")
.pathsToMatch("/admin/**")
.addOpenApiMethodFilter(method -> method.isAnnotationPresent(Admin.class))
.build();
}
If you have only one Docket — remove it and instead add properties to your application.properties:
springdoc.packagesToScan=package1, package2
springdoc.pathsToMatch=/v1, /api/balance/**-
Add bean of
OpenAPItype. See example:
@Bean
public OpenAPI springShopOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI()
.info(new Info().title("SpringShop API")
.description("Spring shop sample application")
.version("v0.0.1")
.license(new License().name("Apache 2.0").url("http://springdoc.org")))
.externalDocs(new ExternalDocumentation()
.description("SpringShop Wiki Documentation")
.url("https://springshop.wiki.github.org/docs"));
}
-
If the swagger-ui/scalar is served behind a proxy:
-
To customise the Swagger UI
-
To hide an operation or a controller from documentation
9. Other resources
10. Sponsor
springdoc-openapi is on Open Collective.
If you ❤️ this project consider becoming a sponsor.
This money is used to cover project expenses and your donation will help the project live and grow successfully.
Thank you to our bronze sponsors!
10.1. Benefits of being a bronze sponsor
Bronze sponsors donate $50 per month to the project, and get the following benefits:
-
You will receive a Sponsor badge 🎖!. Visibility on the front page of springdoc.org in the
welcomepage (about 55,000 views/month on May, 2022). -
“Thank you” tweet from `springdoc team'.
10.2. Benefits of being a silver sponsor
Silver sponsors donate $100 per month to the project, and get the following benefits:
-
Same benefits as bronze sponsors (visibility on main pages, and thank you tweet).
-
The ability to get support for 2
issuesevery month, non transferable. -
If issues are not created by the end of the month, it is lost
10.3. Benefits of being a gold sponsor
Gold sponsors donate $500 per month to the project, and get the following benefits:
-
Same benefits as silver sponsors (visibility on main pages, and thank you tweet).
-
The ability to get support for 10
issuesevery month, non transferable. -
Company logos on all springdoc.org page footers
-
If issues are not created by the end of the month, the remaining ones are lost.
11. Special Thanks
-
Thank you to The Spring Team for sharing all relevant resources around Spring projects.
-
Thanks a lot JetBrains for supporting springdoc-openapi project.
12. F.A.Q
12.1. How can I define multiple OpenAPI definitions in one Spring Boot project?
You can define your own groups of API based on the combination of: API paths and packages to scan. Each group should have a unique groupName.
The OpenAPI description of this group, will be available by default on:
-
http://server:port/context-path/v3/api-docs/groupName
To enable the support of multiple OpenAPI definitions, a bean of type GroupedOpenApi needs to be defined.
For the following Group definition(based on package path), the OpenAPI description URL will be : /v3/api-docs/stores
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi storeOpenApi() {
String paths[] = {"/store/**"};
return GroupedOpenApi.builder().group("stores").pathsToMatch(paths)
.build();
}
For the following Group definition (based on package name), the OpenAPI description URL will be: /v3/api-docs/users
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi userOpenApi() {
String packagesToscan[] = {"test.org.springdoc.api.app68.api.user"};
return GroupedOpenApi.builder().group("users").packagesToScan(packagesToscan)
.build();
}
For the following Group definition(based on path), the OpenAPI description URL will be: /v3/api-docs/pets
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi petOpenApi() {
String paths[] = {"/pet/**"};
return GroupedOpenApi.builder().group("pets").pathsToMatch(paths)
.build();
}
For the following Group definition (based on package name and path), the OpenAPI description URL will be: /v3/api-docs/groups
@Bean
public GroupedOpenApi groupOpenApi() {
String paths[] = {"/v1/**"};
String packagesToscan[] = {"test.org.springdoc.api.app68.api.user", "test.org.springdoc.api.app68.api.store"};
return GroupedOpenApi.builder().group("groups").pathsToMatch(paths).packagesToScan(packagesToscan)
.build();
}
For more details about the usage, you can have a look at the following sample Test:
12.2. How can I configure Swagger UI?
-
The support of the swagger official properties is available on
springdoc-openapi. See Official documentation. -
You can use the same swagger properties in the documentation as Spring Boot properties.
All these properties should be declared with the following prefix: springdoc.swagger-ui
|
12.3. How can I filter the resources documented in the output specification by the provided group?
-
You can use the standard
swagger-uiproperty filter.
springdoc.swagger-ui.filter=group-a
12.4. How can I disable/enable Swagger UI generation based on env variable?
-
This property helps you disable only the UI.
springdoc.swagger-ui.enabled=false
12.5. How can I control the default expansion setting for the operations and tags, in the Swagger UI,
-
You can set this property in your application.yml like so for example:
springdoc.swagger-ui.doc-expansion= none
12.6. How can I change the layout of the swagger-ui?
-
For layout options, you can use swagger-ui configuration options. For example:
springdoc.swagger-ui.layout=BaseLayout
12.7. How can I sort endpoints alphabetically?
-
You can use the following
springdoc-openapiproperties:
#For sorting endpoints alphabetically springdoc.swagger-ui.operationsSorter=alpha #For sorting tags alphabetically springdoc.swagger-ui.tagsSorter=alpha
12.8. How can I disable the try it out button?
-
You have to set the following property:
springdoc.swagger-ui.supportedSubmitMethods=get, put, post, delete, options, head, patch, trace
12.10. How can i apply enumAsRef = true to all enums?
-
Declare the following property:
static {
io.swagger.v3.core.jackson.ModelResolver.enumsAsRef = true;
}
12.11. How can I explicitly set which paths to filter?
-
You can set list of paths to include using the following property:
springdoc.pathsToMatch=/v1, /api/balance/**
12.12. How can I explicitly set which packages to scan?
-
You can set list of packages to include using the following property:
springdoc.packagesToScan=package1, package2
12.13. How can I set Swagger properties programmatically?
These can be set by creating a swaggerUiConfig bean as follows:
@Bean
@Primary
fun swaggerUiConfig(config: SwaggerUiConfigProperties): SwaggerUiConfigProperties {
config.showCommonExtensions = true
config.queryConfigEnabled = true
return config
}
12.14. How can I ignore some field of model?
-
You can use the following annotation on the top of the field that you want to hide:
-
@Schema(hidden = true)
12.15. How can I ignore @AuthenticationPrincipal parameter from spring-security?
-
A solution workaround would be to use:
@Parameter(hidden = true) -
For a project that uses
spring-security, you should add the following dependency, in combination with thespringdoc-openapi-uidependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-security</artifactId>
<version>last.version</version>
</dependency>12.16. Is there a Gradle plugin available?
-
Yes. More details are available, in the gradle plugin section.
12.19. Does springdoc-openapi support Jersey?
-
If you are using JAX-RS and as implementation Jersey (
@Pathfor example), we do not support it. -
We only support exposing Rest Endpoints using Spring managed beans (
@RestControllerfor example). -
You can have a look at swagger-jaxrs2 project:
12.20. Can springdoc-openapi generate API only for @RestController?
-
@RestControlleris equivalent to@Controller+@RequestMappingon the type level. -
For some legacy apps, we are constrained to still support both.
-
If you need to hide the
@Controlleron the type level, in this case, you can use:@Hiddenon controller level. -
Please note this annotation can be also used to hide some methods from the generated documentation.
12.21. Are the following validation annotations supported : @NotEmpty @NotBlank @PositiveOrZero @NegativeOrZero?
-
Yes
12.22. How can I map Pageable (spring-data-commons) object to correct URL-Parameter in Swagger UI?
The support for Pageable of spring-data-commons is available out-of-the box since springdoc-openapi v1.6.0.
For this, you have to combine @ParameterObject annotation with the Pageable type.
Before springdoc-openapi v1.6.0:
-
You can use as well
@ParameterObjectinstead of@PageableAsQueryParamfor HTTPGETmethods.
static {
getConfig().replaceParameterObjectWithClass(org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable.class, Pageable.class)
.replaceParameterObjectWithClass(org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest.class, Pageable.class);
}
-
Another solution, is to configure Pageable manually:
-
you will have to declare the explicit mapping of Pageable fields as Query Params and add the
@Parameter(hidden = true) Pageable pageableon your pageable parameter. -
You should also, declare the annotation
@PageableAsQueryParamprovided byspringdoc-openapion the method level, or declare your own if need to define your custom description, defaultValue, …
-
If you want to disable the support of spring Pageable Type, you can use:
springdoc.model-converters.pageable-converter.enabled=false
The property springdoc.model-converters.pageable-converter.enabled is only available since v1.5.11+
|
12.23. How can I generate enums in the generated description?
-
You could add a property
allowableValues, to@Parameter. For example:
@GetMapping("/example")
public Object example(@Parameter(name = "json", schema = @Schema(description = "var 1", type = "string", allowableValues = {"1", "2"}))
String json) {
return null;
}
-
or you could override
toStringon your enum:
@Override
@JsonValue
public String toString() {
return String.valueOf(action);
}
12.24. How can I deploy springdoc-openapi-ui behind a reverse proxy?
-
If your application is running behind a proxy, a load-balancer or in the cloud, the request information (like the host, port, scheme…) might change along the way. Your application may be running on
10.10.10.10:8080, but HTTP clients should only seeexample.org. -
RFC7239 "Forwarded Headers" defines the Forwarded HTTP header; proxies can use this header to provide information about the original request. You can configure your application to read those headers and automatically use that information when creating links and sending them to clients in HTTP 302 responses, JSON documents or HTML pages. There are also non-standard headers, like
X-Forwarded-Host,X-Forwarded-Port,X-Forwarded-Proto,X-Forwarded-Ssl, andX-Forwarded-Prefix. -
If the proxy adds the commonly used
X-Forwarded-ForandX-Forwarded-Proto headers, setting server.forward-headers-strategy to NATIVE is enough to support those. With this option, the Web servers themselves natively support this feature; you can check their specific documentation to learn about specific behavior. -
You need to make sure the following header is set in your reverse proxy configuration:
X-Forwarded-Prefix -
For example, using Apache 2, configuration:
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Prefix "/custom-path"
-
Then, in your Spring Boot application make sure your application handles this header:
X-Forwarded-For. There are two ways to achieve this:
server.use-forward-headers=true
-
If this is not enough, Spring Framework provides a
ForwardedHeaderFilter. You can register it as a Servlet Filter in your application by setting server.forward-headers-strategy is set to FRAMEWORK. -
Since Spring Boot 2.2, this is the new property to handle reverse proxy headers:
server.forward-headers-strategy=framework-
And you can add the following bean to your application:
@Bean
ForwardedHeaderFilter forwardedHeaderFilter() {
return new ForwardedHeaderFilter();
}
12.26. Adding springdoc-openapi-ui dependency breaks my public/index.html welcome page
-
If you already have static content on your root, and you don’t want it to be overridden by
springdoc-openapi-uiconfiguration, you can just define a custom configuration of theswagger-ui, in order not to override the configuration of your files from in your context-root: -
For example use:
springdoc.swagger-ui.path= /swagger-ui/api-docs.html
12.28. How can I customise the OpenAPI object?
-
You can write your own implementation of
OpenApiCustomizer. -
An example is available on:
@Bean
public OpenApiCustomizer customerGlobalHeaderOpenApiCustomizer() {
return openApi -> openApi.getPaths().values().stream().flatMap(pathItem -> pathItem.readOperations().stream())
.forEach(operation -> operation.addParametersItem(new HeaderParameter().$ref("#/components/parameters/myGlobalHeader")));
}
This bean OpenApiCustomizer will be applied to the Default OpenAPI only.
|
If you need the OpenApiCustomizer to applied to GroupedOpenApi as well, then use GlobalOpenApiCustomizer instead.
12.29. How can I return an empty content as response?
-
It is be possible to handle as return an empty content as response using, one of the following syntaxes:
-
content = @Content -
content = @Content(schema = @Schema(hidden = true)) -
For example:
@Operation(summary = "Get thing", responses = {
@ApiResponse(description = "Successful Operation", responseCode = "200", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json", schema = @Schema(implementation = String.class))),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "Not found", content = @Content),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "401", description = "Authentication Failure", content = @Content(schema = @Schema(hidden = true))) })
@RequestMapping(path = "/testme", method = RequestMethod.GET)
ResponseEntity<String> testme() {
return ResponseEntity.ok("Hello");
}
12.30. How are endpoints with multiple consuming media types supported?
-
An overloaded method on the same class, with the same HTTP Method and path, will have as a result, only one OpenAPI Operation generated.
-
In addition, it’s recommended to have the
@Operationin the level of one of the overloaded methods. Otherwise it might be overridden if it’s declared many times within the same overloaded method.
12.31. How can I get yaml and json (OpenAPI) in compile time?
-
You can use
springdoc-openapi-maven-pluginfor this functionality: -
You can customise the output directory (property outputDir): The default value is: ${project.build.directory}
12.32. What are the ignored types in the documentation?
-
Principal,Locale,HttpServletRequestandHttpServletResponseand other injectable parameters supported by Spring MVC are excluded. -
Full documentation here:
12.33. How can i disable ignored types:
If you don’t want to ignore the types Principal, Locale, HttpServletRequest, and others,:
SpringDocUtils.getConfig().removeRequestWrapperToIgnore(HttpServletRequest.class)
12.34. How do I add authorization header in requests?
-
You should add the
@SecurityRequirementtags to your protected APIs. -
For example:
@Operation(security = { @SecurityRequirement(name = "bearer-key") })
-
And the security definition sample:
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI()
.components(new Components()
.addSecuritySchemes("bearer-key",
new SecurityScheme().type(SecurityScheme.Type.HTTP).scheme("bearer").bearerFormat("JWT")));
}
12.35. Differentiation to Springfox project
-
OAS 3 was released in July 2017, and there was no release of
springfoxto support OAS 3.springfoxcovers for the moment only swagger 2 integration with Spring Boot. The latest release date is June 2018. So, in terms of maintenance there is a big lack of support lately. -
We decided to move forward and share the library that we already used on our internal projects, with the community.
-
The biggest difference with
springfox, is that we integrate new features not covered byspringfox: -
The integration between Spring Boot and OpenAPI 3 standard.
-
We rely on on
swagger-annotationsandswagger-uionly official libraries. -
We support new features on Spring 5, like
spring-webfluxwith annotated and functional style. -
We do our best to answer all the questions and address all issues or enhancement requests
12.36. How do I migrate to OpenAPI 3 with springdoc-openapi
-
There is no relation between
springdoc-openapiandspringfox.If you want to migrate to OpenAPI 3: -
Remove all the dependencies and the related code to springfox
-
Add
springdoc-openapi-uidependency -
If you don’t want to serve the UI from your root path or there is a conflict with an existing configuration, you can just change the following property:
springdoc.swagger-ui.path=/you-path/swagger-ui.html
12.37. How can I set a global header?
-
You may have global parameters with Standard OpenAPI description.
-
If you need the definitions to appear globally (within every group), no matter if the group fulfills the conditions specified on the GroupedOpenApi, you can use OpenAPI Bean.
-
You can define common parameters under parameters in the global components section and reference them elsewhere via
$ref. You can also define global header parameters. -
For this, you can override to OpenAPI Bean, and set the global headers or parameters definition on the components level.
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI(@Value("${springdoc.version}") String appVersion) {
return new OpenAPI()
.components(new Components().addSecuritySchemes("basicScheme", new SecurityScheme().type(SecurityScheme.Type.HTTP).scheme("basic"))
.addParameters("myHeader1", new Parameter().in("header").schema(new StringSchema()).name("myHeader1")).addHeaders("myHeader2", new Header().description("myHeader2 header").schema(new StringSchema())))
.info(new Info()
.title("Petstore API")
.version(appVersion)
.description("This is a sample server Petstore server. You can find out more about Swagger at [http://swagger.io](http://swagger.io) or on [irc.freenode.net, #swagger](http://swagger.io/irc/). For this sample, you can use the api key `special-key` to test the authorization filters.")
.termsOfService("http://swagger.io/terms/")
.license(new License().name("Apache 2.0").url("http://springdoc.org")));
}
12.39. How can I define SecurityScheme?
-
You can use:
@SecuritySchemeannotation. -
Or you can define it programmatically, by overriding OpenAPI Bean:
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI(@Value("${springdoc.version}") String appVersion) {
return new OpenAPI()
.components(new Components().addSecuritySchemes("basicScheme",
new SecurityScheme().type(SecurityScheme.Type.HTTP).scheme("basic")))
.info(new Info().title("SpringShop API").version(appVersion)
.license(new License().name("Apache 2.0").url("http://springdoc.org")));
}
12.40. How can I hide an operation or a controller from documentation?
-
You can use
@io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Hiddenannotation at@RestController,@RestControllerAdviceand method level -
The
@Hiddenannotation on exception handler methods, is considered when building generic (error) responses from@ControllerAdviceexception handlers. -
Or use:
@Operation(hidden = true)
12.41. How to configure global security schemes?
-
For global SecurityScheme, you can add it inside your own OpenAPI definition:
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI().components(new Components()
.addSecuritySchemes("basicScheme", new SecurityScheme()
.type(SecurityScheme.Type.HTTP).scheme("basic"))).info(new Info().title("Custom API")
.version("100")).addTagsItem(new Tag().name("mytag"));
}
12.42. Can I use spring property with swagger annotations?
-
The support of spring property resolver for
@Info:title*description*version*termsOfService -
The support of spring property resolver for
@Info.license:name*url -
The support of spring property resolver for
@Info.contact:name*email*url -
The support of spring property resolver for
@Operation:description*summary -
The support of spring property resolver for
@Parameter:description*name -
The support of spring property resolver for
@ApiResponse:description -
Its also possible to declare security URLs for
@OAuthFlow:openIdConnectUrl*authorizationUrl*refreshUrl*tokenUrl -
The support of spring property resolver for
@Schema:name*title*description, by settingspringdoc.api-docs.resolve-schema-propertiestotrue
12.43. How is server URL generated?
-
Generating automatically server URL may be useful, if the documentation is not present.
-
If the server annotations are present, they will be used instead.
12.44. How can I disable springdoc-openapi cache?
-
By default, the OpenAPI description is calculated once, and then cached.
-
Sometimes the same swagger-ui is served behind internal and external proxies. some users want the server URL, to be computed on each http request.
-
In order to disable springdoc cache, you will have to set the following property:
springdoc.cache.disabled= true
12.45. How can I expose the mvc api-docs endpoints without using the swagger-ui?
-
You should use the
springdoc-openapi-coredependency only:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-webmvc-core</artifactId>
<version>latest.version</version>
</dependency>12.46. How can I disable springdoc-openapi endpoints?
-
Use the following property:
springdoc.api-docs.enabled=false
12.47. How can I hide Schema of the the response?
-
To hide the response element, using
@Schemaannotation, as follows, at operation level:
@Operation(responses = @ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", content = @Content(schema = @Schema(hidden = true))))
-
Or directly at
@ApiResponseslevel:
@ApiResponses(value = {@ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", content = @Content(schema = @Schema(hidden = true))) })
OR
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "Not found", content = @Content)
12.48. What is the URL of the swagger-ui, when I set a different context-path?
-
If you use different context-path:
server.servlet.context-path= /foo
-
The
swagger-uiwill be available on the following URL:-
http://server:port/foo/swagger-ui.html
-
12.49. Can I customize OpenAPI object programmatically?
-
You can Define your own OpenAPI Bean: If you need the definitions to appear globally (within every group), no matter if the group fulfills the conditions specified on the GroupedOpenApi, you can use OpenAPI Bean.
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI(@Value("${springdoc.version}") String appVersion) {
return new OpenAPI()
.components(new Components().addSecuritySchemes("basicScheme",
new SecurityScheme().type(SecurityScheme.Type.HTTP).scheme("basic")))
.info(new Info().title("SpringShop API").version(appVersion)
.license(new License().name("Apache 2.0").url("http://springdoc.org")));
}
-
If you need the definitions to appear within a specific group, and respect the conditions specified on the GroupedOpenApi, you can add OpenApiCustomiser to your GroupedOpenApi definition.
GroupedOpenApi.builder().group("users").pathsToMatch(paths).packagesToScan(packagedToMatch).addOpenApiCustomiser(customerGlobalHeaderOpenApiCustomiser())
.build()
@Bean
public OpenApiCustomiser customerGlobalHeaderOpenApiCustomiser() {
return openApi -> openApi.path("/foo",
new PathItem().get(new Operation().operationId("foo").responses(new ApiResponses()
.addApiResponse("default", new ApiResponse().description("")
.content(new Content().addMediaType("fatz", new MediaType()))))));
}
12.50. Where can I find the source code of the demo applications?
-
The source code of the application is available at the following GitHub repository:
12.53. Is file upload supported?
-
The library supports the main file types:
MultipartFile,@RequestPart,FilePart
12.55. Why my parameter is marked as required?
-
Any
@GetMappingparameters is marked as required, even if@RequestParamis missing. -
You can add
@Parameter(required=false)annotation if you need different behaviour. -
Query parameters with
defaultValuespecified are marked as required.
12.56. How are overloaded methods with the same endpoints, but with different parameters
-
springdoc-openapirenders these methods as a single endpoint. It detects the overloaded endpoints, and generates parameters.schema.oneOf.
12.57. What is a proper way to set up Swagger UI to use provided spec.yml?
-
With this property, all the
springdoc-openapiauto-configuration beans are disabled:
springdoc.api-docs.enabled=false
-
Then enable the minimal Beans configuration, by adding this Bean:
@Bean
SpringDocConfiguration springDocConfiguration(){
return new SpringDocConfiguration();
}
@Bean
SpringDocConfigProperties springDocConfigProperties() {
return new SpringDocConfigProperties();
}
@Bean
ObjectMapperProvider objectMapperProvider(SpringDocConfigProperties springDocConfigProperties){
return new ObjectMapperProvider(springDocConfigProperties);
}
-
Then configure, the path of your custom UI yaml file.
springdoc.swagger-ui.url=/api-docs.yaml
12.58. Is there a way to send authorization header through the @Parameter tag?
-
The OpenAPI 3 specification does not allow explicitly adding Authorization header.
Note: Header parameters named Accept, Content-Type and Authorization are not allowed. To describe these headers -
For more information, you can read:
12.59. My Rest Controller using @Controller annotation is ignored?
-
This is the default behaviour if your
@Controllerdoesn’t have annotation@ResponseBody -
You can change your controllers to
@RestControllers. Or add@ResponseBody+@Controller. -
If its not possible, you can configure springdoc to scan you additional controller using SpringDocUtils. For example:
static {
SpringDocUtils.getConfig().addRestControllers(HelloController.class);
}
12.60. How can I define groups using application.yml?
-
You can load groups dynamically using spring-boot configuration files.
-
Note that, for this usage, you don’t have to declare the GroupedOpenApi Bean.
-
You need to declare the following properties, under the prefix springdoc.group-configs.
-
For example:
springdoc.group-configs[0].group=users springdoc.group-configs[0].paths-to-match=/user/** springdoc.group-configs[0].packages-to-scan=test.org.springdoc.api
-
The list of properties under this prefix, are available here:
12.61. How can I extract fields from parameter object?
-
You can use springdoc annotation @ParameterObject.
-
Request parameter annotated with @ParameterObject will help adding each field of the parameter as a separate request parameter.
-
This is compatible with Spring MVC request parameters mapping to POJO object.
-
This annotation does not support nested parameter objects.
-
POJO object must contain getters for fields with mandatory prefix
get. Otherwise, the swagger documentation will not show the fields of the annotated entity.
12.62. How to Integrate Open API 3 with Spring project (not Spring Boot)?
When your application is using spring without (spring-boot), you need to add beans and auto-configuration that are natively provided in spring-boot.
For example, lets assume you want load the swagger-ui in spring-mvc application:
-
You mainly, need to add the springdoc-openapi module
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-ui</artifactId>
<version>last.version</version>
</dependency>-
If you don’t have the spring-boot and spring-boot-autoconfigure dependencies, you need to add them. And pay attention to the compatibility matrix, between you spring.version and spring-boot.version. For example, in this case (spring.version=5.1.12.RELEASE):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>2.1.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>2.1.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>-
Scan for the
springdoc-openapi'auto-configuration classes that spring-boot automatically loads for you. -
Depending on your module, you can find them on the file:
spring.factoriesof eachspringdoc-openapimodule.
@EnableWebMvc
public class AppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
WebApplicationContext context = getContext();
servletContext.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(context));
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher = servletContext.addServlet("RestServlet",
new DispatcherServlet(context));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/*");
}
private AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext getContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.scan("rest");
context.register(this.getClass(), org.springdoc.webmvc.ui.SwaggerConfig.class,
org.springdoc.core.SwaggerUiConfigProperties.class, org.springdoc.core.SwaggerUiOAuthProperties.class,
org.springdoc.webmvc.core.SpringDocWebMvcConfiguration.class,
org.springdoc.webmvc.core.MultipleOpenApiSupportConfiguration.class,
org.springdoc.core.SpringDocConfiguration.class, org.springdoc.core.SpringDocConfigProperties.class,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration.class);
return context;
}
}
-
Depending on your module, you can find them on the file:
spring.factoriesof eachspringdoc-openapimodule. -
For groups usage make sure your
GroupedOpenApiBeans are scanned. -
If additionally, you are using custom
context path:/my-servlet-path. Make sure you declare the following property:
spring.mvc.servlet.path=/my-servlet-path
12.63. How can I use the last springdoc-openapi SNAPSHOT ?
-
For testing purposes only, you can test temporarily using the last
springdoc-openapiSNAPSHOT -
To achieve that, configure your pom.xml file with the following
<repositories>section:
<repositories>
<repository>
<name>Central Portal Snapshots</name>
<id>central-portal-snapshots</id>
<url>https://central.sonatype.com/repository/maven-snapshots/</url>
<releases>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>12.64. How can I use enable springdoc-openapi MonetaryAmount support?
-
If an application wants to enable the
springdoc-openapisupport, it declares:
SpringDocUtils.getConfig().replaceWithClass(MonetaryAmount.class, org.springdoc.core.converters.models.MonetaryAmount.class);
-
Another solution, without using springdoc-openapi MonetaryAmount, would be:
SpringDocUtils.getConfig().replaceWithSchema(MonetaryAmount.class, new ObjectSchema()
.addProperties("amount", new NumberSchema()).example(99.96)
.addProperties("currency", new StringSchema().example("USD")));
12.65. How can i aggregate external endpoints (exposing OPENAPI 3 spec) inside one single application?
The properties springdoc.swagger-ui.urls.*, are suitable to configure external (/v3/api-docs url).
For example, if you want to aggregate all the endpoints of other services, inside one single application.
IMPORTANT: Don’t forget that CORS needs to be enabled as well.
12.66. How can use custom json/yml file instead of generated one?
If your file open-api.json, contains the OpenAPI documentation in OpenAPI 3 format. Then simply declare: The file name can be anything you want, from the moment your declaration is consistent yaml or json OpenAPI Spec.
springdoc.swagger-ui.url=/open-api.jsonThen the file open-api.json, should be located in: src/main/resources/static No additional configuration is needed.
12.67. How can i enable CSRF support?
If you are using standard headers. (For example, using spring-security headers) If the CSRF Token is required, swagger-ui automatically sends the new XSRF-TOKEN during each HTTP REQUEST.
If your XSRF-TOKEN isn’t standards-based, you can use a requestInterceptor to manually capture and attach the latest xsrf token to requests programmatically via spring resource transformer:
Starting from release v1.4.4 of springdoc-openapi, a new property is added to enable CSRF support, while using standard header names:
springdoc.swagger-ui.csrf.enabled=true12.68. How can i disable the default swagger petstore URL?
You can use the following property:
springdoc.swagger-ui.disable-swagger-default-url=true12.69. Is @PageableDefault supported, to enhance the OpenAPI 3 documentation?
Yes, you can use it in conjunction with @ParameterObject annotation.
Also, the spring-boot spring.data.web. and spring.data.rest.default. properties are supported since v1.4.5
12.70. How can I make spring security login-endpoint visible?
You can use the following property:
springdoc.show-login-endpoint=true12.71. How can I show schema definitions even if the schema is not referenced?
You can use the following property:
springdoc.remove-broken-reference-definitions=false12.72. How to override @Deprecated?
The whole idea of springdoc-openapi is to get your documentation the closest to the code, with minimal code changes.
If the code contains @Deprecated, sprindoc-openapi will consider its schema as Deprecated as well.
If you want to declare a field on swagger as non deprecated, even with the java code, the field contains @Depreacted,
You can use the following property that is available since release v1.4.3:
springdoc.model-converters.deprecating-converter.enabled=false12.73. How can i display a method that returns ModelAndView?
You can use the following property:
springdoc.model-and-view-allowed=true12.74. How can i have pretty-printed output of the OpenApi specification?
You can use the following property:
springdoc.writer-with-default-pretty-printer=true12.75. How can i define different schemas for the same class?
Complex objects are always resolved as a reference to a schema defined in components.
For example, let’s consider a Instance class with an workAddress and homeAddress attribute of type Address:
public class PersonDTO {
@JsonProperty
private String email;
@JsonProperty
private String firstName;
@JsonProperty
private String lastName;
@Schema(ref = "WorkAddressSchema")
@JsonProperty
private Address workAddress;
@Schema(ref = "HomeAddressSchema")
@JsonProperty
private Address homeAddress;
}
public class Address {
@JsonProperty
private String addressName;
}
If you want to define two different schemas for this class, you can set up 2 different schemas as follow:
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI().components(new Components()
.addSchemas("WorkAddressSchema", getSchemaWithDifferentDescription(Address.class, "work Address"))
.addSchemas("HomeAddressSchema", getSchemaWithDifferentDescription(Address.class, "home Address")));
}
private Schema getSchemaWithDifferentDescription(Class className, String description) {
ResolvedSchema resolvedSchema = ModelConverters.getInstance()
.resolveAsResolvedSchema(
new AnnotatedType(className).resolveAsRef(false));
return resolvedSchema.schema.description(description);
}
12.76. How can i define different description for a class attribute depending on usage?
For example, let’s consider a Instance class with an email attribute:
public class PersonDTO {
@JsonProperty
private String email;
@JsonProperty
private String firstName;
@JsonProperty
private String lastName;
}
If you want to define two different description for the email, you can set up 2 different schemas as follow:
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI().components(new Components()
.addSchemas("PersonDTO1", getFieldSchemaWithDifferentDescription(PersonDTO.class, "work email"))
.addSchemas("PersonDTO2", getFieldSchemaWithDifferentDescription(PersonDTO.class, "home email")));
}
private Schema getFieldSchemaWithDifferentDescription(Class className, String description) {
ResolvedSchema resolvedSchema = ModelConverters.getInstance()
.resolveAsResolvedSchema(
new AnnotatedType(className).resolveAsRef(false));
return resolvedSchema.schema.addProperties("email", new StringSchema().description(description));
}
12.77. Customizing swagger static resources
You can customize swagger documentation static resources located in META-INF/resources/webjars/swagger-ui/{swagger.version}/. The list of resources includes:
-
index.html -
swagger-ui-bundle.js -
swagger-ui.css -
swagger-ui-standalone-preset.js -
swagger-ui.css.map -
swagger-ui-bundle.js.map -
swagger-ui-standalone-preset.js.map -
favicon-32x32.png
To do this, you need to extend the implementation of SwaggerIndexPageTransformer
public class SwaggerCodeBlockTransformer
extends SwaggerIndexPageTransformer {
// < constructor >
@Override
public Resource transform(HttpServletRequest request,
Resource resource,
ResourceTransformerChain transformer)
throws IOException {
if (resource.toString().contains("swagger-ui.css")) {
final InputStream is = resource.getInputStream();
final InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr)) {
final String css = br.lines().collect(Collectors.joining());
final byte[] transformedContent = css.replace("old", "new").getBytes();
return new TransformedResource(resource, transformedContent);
} // AutoCloseable br > isr > is
}
return super.transform(request, resource, transformer);
}
}
Next, add transformer @Bean to your @Configuration
@Configuration
public class OpenApiConfig {
@Bean
public SwaggerIndexTransformer swaggerIndexTransformer(
SwaggerUiConfigProperties a,
SwaggerUiOAuthProperties b,
SwaggerUiConfigParameters c,
SwaggerWelcomeCommon d) {
return new SwaggerCodeBlockTransformer(a, b, c, d);
}
}
Illustrative example

12.78. What is the compatibility matrix of springdoc-openapi with spring-boot ?
springdoc-openapi is compatible with spring-boot 1 and spring-boot 2.
In general, you should only pick the last stable version as per today 1.8.0.
More precisely, this the exhaustive list of spring-boot versions against which springdoc-openapi has been built:
| spring-boot Versions | Minimum springdoc-openapi Versions |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.79. Why am i getting an error: Swagger UI unable to render definition, when overriding the default spring registered HttpMessageConverter?
When overriding the default spring-boot registered HttpMessageConverter, you should have ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter registered as well to have proper springdoc-openapi support.
converters.add(new ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter());
converters.add(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(jacksonBuilder.build()));
Order is very important, when registering HttpMessageConverters.
|